Think back to the year 2000. The world looked completely different than it does today. So many gadgets, apps, and services we rely on every single day simply did not exist back then. From the phone in your pocket to the way you listen to music, technology has transformed our lives in ways that would have seemed like science fiction just a quarter century ago.
1. Smartphones (as we know them today)
Before 2007, nobody had ever swiped through apps on a touchscreen phone. The iPhone changed everything when it launched that year, creating a whole new category of device.
Earlier mobile phones could make calls and send texts, but they had tiny screens and physical keyboards. You couldn’t browse the web easily, take decent photos, or download thousands of apps. The modern smartphone combined a computer, camera, music player, and phone into one sleek package.
Today, billions of people around the world depend on smartphones for everything from schoolwork to staying connected with friends. These powerful pocket computers have become so essential that many people check them over 100 times per day. Life without a smartphone now feels almost impossible for most of us.
2. Social Media Platforms
Imagine not being able to scroll through posts from friends or watch funny videos online. That was reality in 2000, before any major social media platforms existed.
Facebook launched in 2004, originally just for college students. YouTube came along in 2005, letting anyone upload and share videos. Twitter started in 2006 with its short message format, and Instagram arrived in 2010 with its focus on photos.
These platforms completely changed how people communicate, share news, and express themselves. Friendships now exist entirely online, and viral videos can make someone famous overnight. Social media has connected the world in amazing ways, though it also brought new challenges like cyberbullying and misinformation. For better or worse, these platforms have reshaped modern society in profound ways that continue evolving every day.
3. Streaming Services
Remember when watching a movie meant driving to a rental store? Netflix started as a DVD-by-mail service, but everything changed when it launched streaming in 2007.
Suddenly, thousands of movies and shows became available instantly on your TV or computer. No more late fees, no more rewinding tapes. Spotify followed in 2008, doing the same thing for music. Instead of buying individual songs or albums, you could stream millions of tracks for one monthly fee.
Streaming has practically killed off video rental stores and dramatically reduced physical media sales. Most people now watch shows by binge-watching entire seasons in one sitting, which was never possible before. The convenience of having endless entertainment at your fingertips has fundamentally changed how we consume media and spend our free time.
4. Ride-sharing Apps
Getting a ride from a stranger using your phone would have sounded dangerous and crazy in 2000. Yet that is exactly what millions of people do every day now.
Uber launched in 2009, followed by Lyft in 2012. These apps connected riders with drivers using GPS technology and cashless payments. You could see exactly where your driver was, how much the trip would cost, and rate your experience afterward.
Traditional taxi services struggled to compete with the convenience and lower prices. Ride-sharing made it easier to get around without owning a car, especially in cities. The concept even expanded to food delivery and package shipping. These apps created a whole new economy where anyone with a car could earn money driving people around, though debates continue about worker rights and fair pay.
5. Tablets
Laptop computers existed 25 years ago, but tablets as we know them did not. Apple’s iPad launched in 2010 and created massive excitement about this new category of device.
Tablets offered touchscreen computing in a thin, light package perfect for browsing the web, reading, or watching videos on the couch. They filled the gap between smartphones and laptops beautifully. Kids especially loved them for games and educational apps, while adults found them great for casual computing tasks.
Skeptics initially wondered who would buy a tablet when they already had a phone and computer. Those doubts vanished quickly as millions of iPads and Android tablets flew off shelves. Schools started using them in classrooms, restaurants used them for menus, and doctors used them to access patient records. The tablet revolution proved there was room for a third type of computing device in our lives.
6. Smartwatches
Watches used to do just one thing: tell time. Now they track your heart rate, count your steps, show text messages, and even make phone calls.
The modern smartwatch era began with Pebble in 2013, but the Apple Watch in 2015 really made them mainstream. These tiny computers on your wrist can monitor your health, guide you with GPS directions, and let you pay for things without pulling out your wallet.
Fitness enthusiasts love tracking their workouts in real time. Busy professionals appreciate getting important notifications without constantly checking their phones. Some smartwatches can even detect falls or irregular heartbeats and alert emergency services. What started as a cool gadget has become a genuine health and safety tool for many people, especially older adults who value the medical monitoring features.
7. Voice Assistants
Talking to your devices and having them understand you seemed like pure science fiction not long ago. Siri changed that when it launched on the iPhone in 2011.
Amazon’s Alexa arrived in 2014 inside the Echo smart speaker, followed by Google Assistant in 2016. These artificial intelligence helpers could answer questions, play music, set timers, control smart home devices, and handle countless other tasks, all through voice commands.
Voice assistants made technology more accessible, especially for people who struggle with typing or small screens. Families use them to settle dinner table debates, kids ask them homework questions, and busy cooks use them hands-free while preparing meals. The technology keeps improving, understanding more languages and accents every year. Though sometimes hilariously wrong, voice assistants have become trusted members of many households.
8. Electric Cars for the Mass Market
Electric vehicles existed decades ago, but they were slow, expensive, and had terrible range. Nobody thought of them as practical everyday cars until Tesla came along.
The Tesla Model S launched in 2012 as the first long-range electric vehicle regular people could actually buy and use. It proved electric cars could be fast, stylish, and drive hundreds of miles on a single charge. Other automakers took notice and started developing their own electric models.
Today, electric cars are everywhere, with charging stations popping up in parking lots and along highways. They produce zero emissions, cost less to maintain than gas cars, and offer instant acceleration that surprises new drivers. Environmental concerns and government incentives have pushed more people to consider going electric. The automotive industry is rapidly shifting away from gasoline engines toward an all-electric future.
9. Wi-Fi as a Household Standard
Connecting to the internet used to mean plugging a cable into your computer. Wireless internet existed 25 years ago, but it was rare, expensive, and slow.
The 802.11g Wi-Fi standard launched in 2003, offering faster speeds and better range. Cheap home routers soon flooded the market, making wireless internet affordable for average families. Suddenly, you could use your laptop anywhere in the house, not just at a desk.
Wi-Fi became essential as more devices needed internet connections. Smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, gaming consoles, and even refrigerators now rely on Wi-Fi. Coffee shops and restaurants started offering free Wi-Fi to attract customers. Public Wi-Fi networks appeared in airports, libraries, and parks. The ability to connect wirelessly has become so expected that people get frustrated when they visit places without it.
10. QR Codes in Daily Life
Those weird square barcodes are everywhere now, but they were invented in the 1990s for tracking car parts in factories. Nobody used them in daily life until smartphones became common after 2010.
QR codes exploded in popularity because smartphone cameras could scan them instantly, opening websites or displaying information without typing. Restaurants started using them for menus, especially during the pandemic. Stores use them for mobile payments and coupons.
You will find QR codes on product packaging, museum exhibits, business cards, and even gravestones now. They bridge the physical and digital worlds effortlessly. Some people find them annoying, preferring traditional menus and signs. Others love the convenience of instantly accessing information with a quick scan. Love them or hate them, QR codes have become a permanent part of modern life that shows no signs of disappearing.
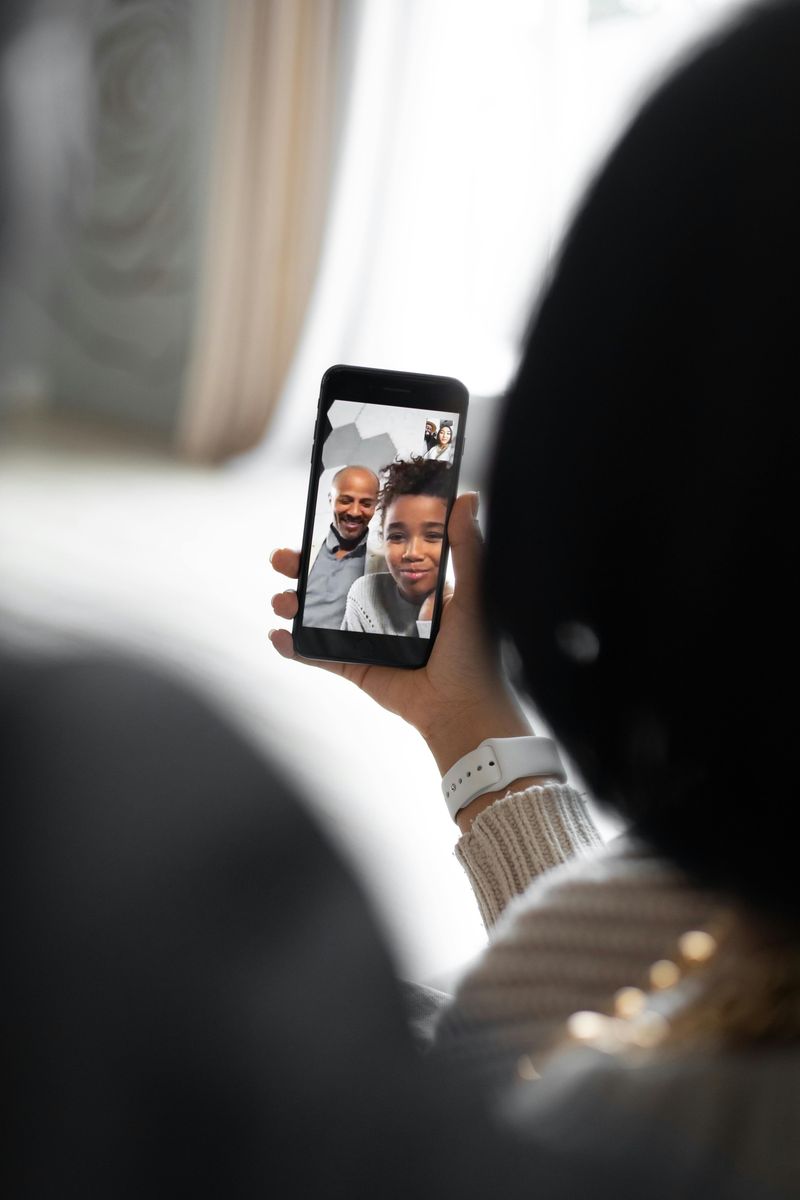
11. Video Calling as Normal Communication
Video phones appeared in science fiction movies, but actually using one was rare and expensive until recently. Skype launched in 2003, making internet video calls possible, but the technology really took off after 2010 when smartphones and better internet made it easy.
FaceTime, Zoom, and other apps turned video calling into something completely normal. Grandparents video chat with grandkids across the country. Friends have virtual hangouts. Remote workers attend meetings from home in their pajamas.
The pandemic in 2020 made video calling absolutely essential for work, school, and staying connected with loved ones. What once felt awkward and futuristic became as natural as making a phone call. Seeing someone’s face while talking adds so much more than just hearing their voice. Video calling has made the world feel smaller and kept relationships strong across any distance.
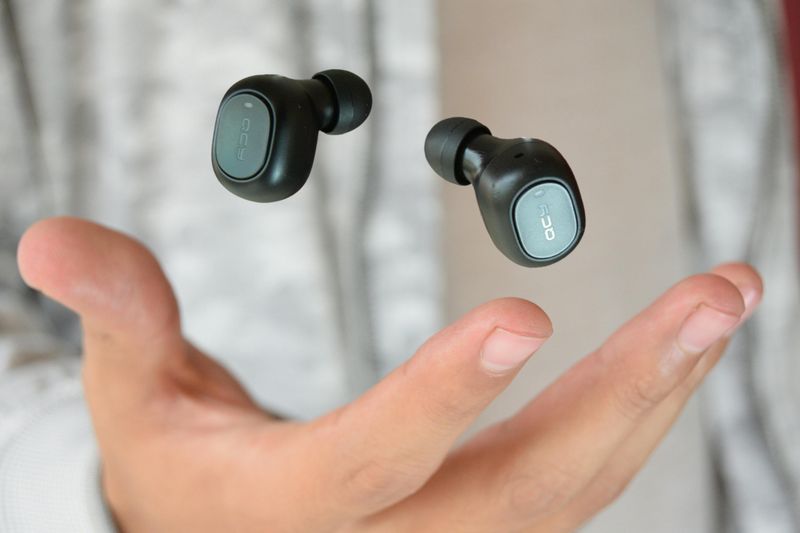
12. Bluetooth Earbuds
Tangled headphone wires were once an unavoidable annoyance. Early Bluetooth earbuds appeared after 2004, but they were clunky, expensive, and had poor sound quality.
Everything changed when Apple released AirPods in 2016. These tiny wireless earbuds worked seamlessly with iPhones and offered surprisingly good sound. Other companies quickly released competing models at various price points, making wireless earbuds accessible to everyone.
Bluetooth earbuds freed people from the tyranny of wires getting caught on doorknobs and tangled in pockets. Runners and gym-goers especially appreciated the freedom of movement. The sound quality kept improving, and battery life got longer. Some models now include noise cancellation that blocks out the world around you. Walking down any street today, you will see countless people with small white buds in their ears, living in their own personal audio bubbles.
13. Cloud Storage Services
Saving files meant keeping them on your computer’s hard drive or burning them to CDs. If your computer crashed, you lost everything unless you had backup copies.
Dropbox launched in 2007, offering online storage that synced across all your devices automatically. Google Drive followed in 2012 with generous free storage. These cloud services meant your files lived safely on internet servers, accessible from any device anywhere.
Students can now start homework on a school computer and finish it on their phone during the bus ride home. Photos automatically back up from your phone so you never lose precious memories. Families share photo albums, and coworkers collaborate on documents in real time. Cloud storage has made the concept of saving files to specific devices feel old-fashioned. Everything lives in the cloud now, always available whenever you need it.
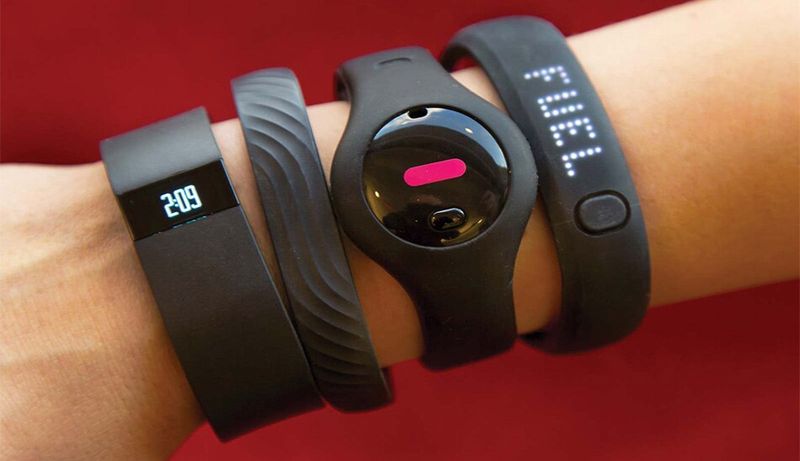
14. Fitness Trackers
Want to know how many steps you took today? Twenty-five years ago, you would need to count them yourself or wear a clunky pedometer. Fitbit launched in 2009 and started the fitness tracking revolution.
These wearable devices count steps, monitor heart rate, track sleep patterns, and calculate calories burned throughout the day. They motivated millions of people to move more by turning fitness into a game with goals and achievements. Friendly competitions with friends made exercise more fun.
Fitness trackers revealed surprising truths about our activity levels and sleep quality. Many people discovered they were far less active than they thought. The data helped users make healthier choices and spot patterns affecting their wellbeing. Doctors even started using fitness tracker data to monitor patients. What began as a trendy gadget became a legitimate health tool that helps people live longer, healthier lives.
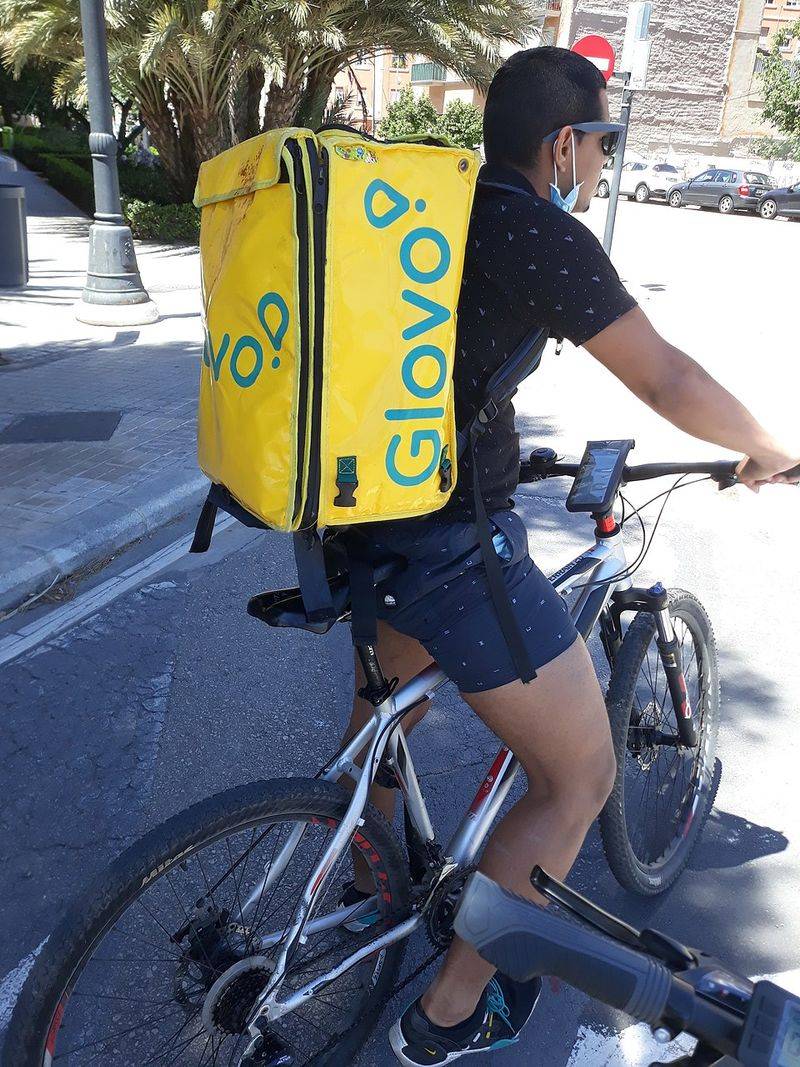
15. Online Food Delivery Apps
Ordering food for delivery meant calling restaurants and hoping they delivered to your address. You needed cash ready for the driver, and tracking your order was impossible.
DoorDash launched in 2013, Uber Eats in 2014, and the Grubhub app in 2010. These services connected customers with restaurants and independent delivery drivers through easy-to-use apps. You could browse menus from dozens of restaurants, pay digitally, and watch your food travel to you on a map in real time.
Suddenly, almost any restaurant became available for delivery, even places that never offered it before. Late-night cravings and lazy Sunday mornings got infinitely easier to satisfy. The pandemic made these apps essential when dining rooms closed. Critics worry about high fees and treatment of delivery drivers, but the convenience has made food delivery apps a permanent part of modern life.
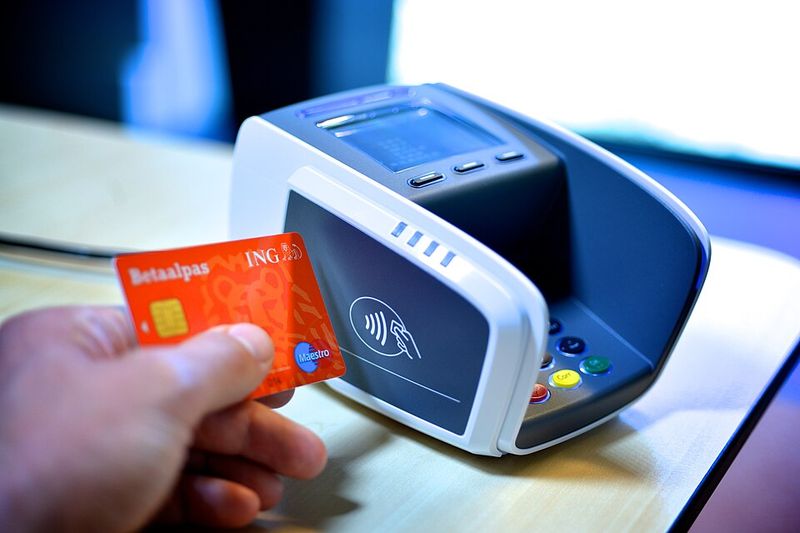
16. Contactless Payment (NFC) for Consumers
Paying for things meant pulling out cash or swiping a credit card. The first smartphones with NFC (Near Field Communication) technology appeared between 2006 and 2010, but contactless payment did not really catch on until Apple Pay launched in 2014.
Now you can simply tap your phone or smartwatch against a payment terminal and you are done in seconds. No need to carry a wallet full of cards. The technology is secure, using encryption and biometric authentication like fingerprints or face recognition.
Contactless payment became especially popular during the pandemic when people wanted to avoid touching shared surfaces. It is faster than chip cards and more convenient than carrying cash. Many stores now prefer contactless payments because they speed up checkout lines. The technology has made forgetting your wallet at home much less of a disaster.
17. DNA Home Testing Kits
Learning about your ancestry or genetic health risks required expensive testing through a doctor. Then 23andMe started offering consumer genetic testing in 2006, followed by AncestryDNA in 2012.
These companies mail you a kit where you spit in a tube and send it back. A few weeks later, you get detailed reports about your ethnic background, potential relatives, and health predispositions. People have discovered unknown siblings, traced their family trees back centuries, and learned about genetic conditions they might pass to their children.
The tests sparked a genealogy craze as millions of people explored their roots. Some discoveries brought joy, while others caused family drama when unexpected relationships came to light. Privacy concerns exist about companies storing your genetic data. Despite controversies, DNA testing has given ordinary people access to genetic information that was once impossible to obtain.
18. E-readers
Book lovers used to need suitcases to bring reading material on vacation. Heavy hardcovers and thick paperbacks took up space and added weight to bags.
Amazon’s Kindle launched in 2007 and changed reading forever. This thin device could store thousands of books using special e-ink screens that looked like real paper and did not strain your eyes. You could download new books instantly without visiting a bookstore. Adjustable text size helped people with vision problems enjoy reading again.
Libraries started offering digital book lending, and students could carry all their textbooks on one light device. Environmentalists appreciated saving trees. Some readers still prefer physical books for the tactile experience and the smell of paper. But e-readers have carved out a permanent place in reading culture, making books more accessible and portable than ever imagined.
19. Streaming Music Players
Music lovers once built massive CD collections or downloaded individual songs from iTunes. Spotify changed everything when it became globally available after 2008.
For one monthly fee, you suddenly had access to virtually every song ever recorded. No more buying albums hoping you would like more than one song. You could create unlimited playlists, discover new artists through recommendations, and listen offline by downloading songs to your device.
The music industry initially resisted streaming, worried about losing sales revenue. Artists debated whether tiny streaming payments fairly compensated their work. But listeners embraced the convenience and variety enthusiastically. Other services like Apple Music and Pandora joined the competition. Streaming has fundamentally transformed how we discover, share, and enjoy music. Physical music sales have plummeted, but more people listen to more diverse music than ever before in history.
20. High-Quality Phone Cameras
Early mobile phones had cameras, but the photos looked terrible and grainy. You still needed a separate digital camera for pictures worth keeping.
True smartphone cameras with autofocus, video recording, and high-resolution sensors emerged after 2007 with the iPhone and improved dramatically by 2010. Each new phone generation brought better lenses, more megapixels, and clever software that made photos look professional. Night mode, portrait mode, and computational photography turned phones into incredibly capable cameras.
Dedicated camera sales collapsed as phone cameras got good enough for most people. Instagram and Snapchat thrived because everyone always had a great camera in their pocket. Important moments get captured and shared instantly now. Professional photographers even use phones for serious work sometimes. The best camera is the one you have with you, and now that camera is pretty amazing.