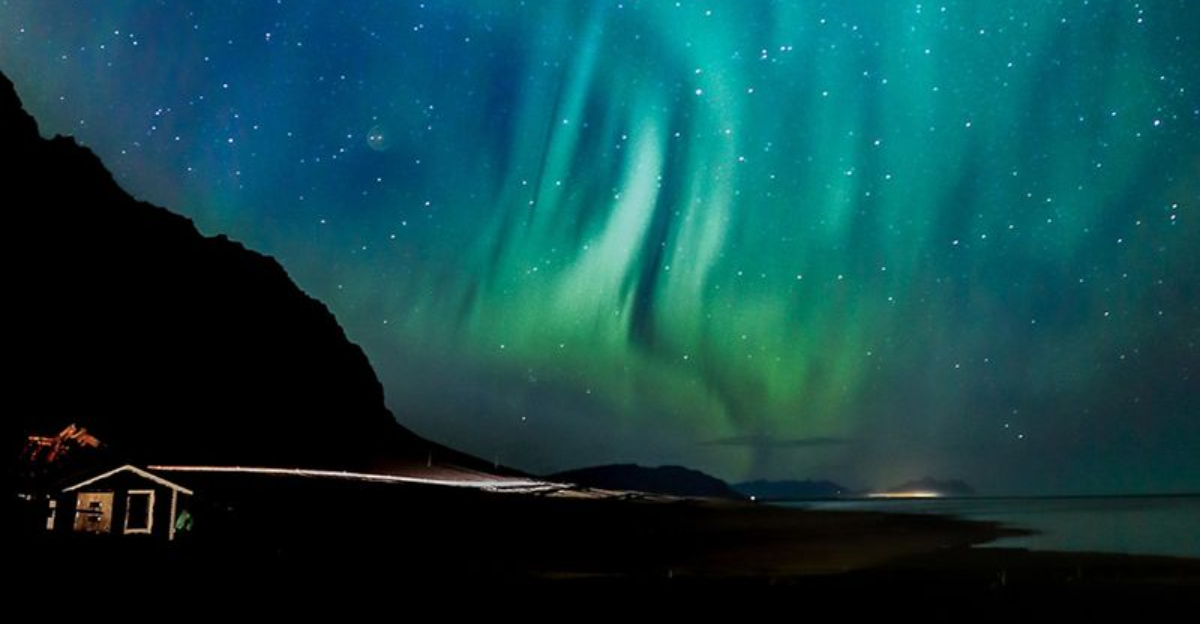
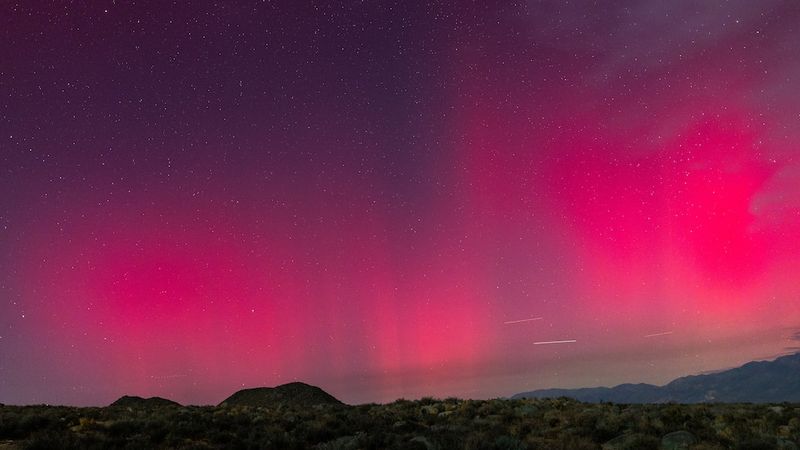
Get ready for a spectacular light show in the sky! This week, powerful solar storms are headed toward Earth, bringing with them the magical Northern Lights that could dance across the night sky in places that don’t normally see them. These colorful displays happen when charged particles from the Sun collide with gases in our atmosphere, creating ribbons of green, pink, and purple light. Whether you’re a seasoned aurora chaser or hoping to catch your first glimpse, this week offers an exciting opportunity to witness one of nature’s most breathtaking phenomena.
What Causes These Dazzling Solar Storms
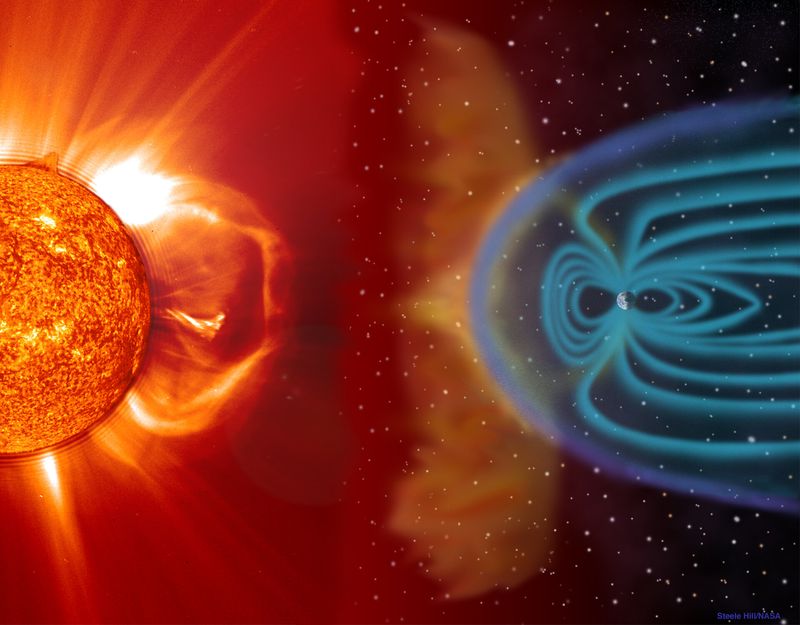
Between October 11 and 13, 2025, the Sun unleashed multiple powerful bursts called coronal mass ejections from a particularly active sunspot region. Think of these like giant bubbles of magnetized plasma shooting off the Sun’s surface at incredible speeds. When these solar particles slam into Earth’s magnetic field, they create the perfect recipe for aurora displays.
Right now, the solar wind is racing toward us at about 507 kilometers per second—that’s over a million miles per hour! Scientists measure something called the Bz component, which shows how the Sun’s magnetic field is oriented. When it dips southward (negative), it’s like opening a door for particles to flow into our atmosphere. This combination of fast-moving particles and favorable magnetic conditions means we’re in for quite a show, with geomagnetic storm levels reaching G2 (moderate) intensity this week.
Where You Might Spot the Auroras
Usually, you’d need to travel to Alaska, Iceland, or northern Canada to catch the Northern Lights. But here’s the exciting part: this week’s geomagnetic storm could push the aurora zone much farther south than normal. States like Washington, Montana, the Dakotas, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan, Maine, and possibly even New York and Idaho might get lucky!
Your best bet is heading away from bright city lights to somewhere dark and open. Face north and scan the horizon—sometimes the lights start as a faint glow before erupting into dancing curtains of color. Northern regions like Scandinavia and Canada still have the highest odds, but mid-latitude locations are definitely in the game this time. Keep checking aurora forecast websites and local weather conditions throughout the week, because timing matters just as much as location does.
Best Times and Tips for Viewing Success
Timing can make or break your aurora hunt. The sweet spot typically falls between 10 p.m. and 2 a.m. local time, when the sky is darkest and geomagnetic activity often peaks. However, auroras don’t follow strict schedules, so keeping watch throughout the night increases your chances considerably.
Here’s a pro tip: bring a camera with long exposure capabilities. Digital cameras often capture colors and details that your eyes might miss, especially fainter green glows. Check real-time aurora maps and apps like SpaceWeatherLive or NOAA’s Aurora Dashboard—they’ll alert you when activity spikes. Clear skies are absolutely essential, so monitor weather forecasts closely. Even a few scattered clouds can ruin the view. Dress warmly in layers, pack hot beverages, and find a comfortable spot with an unobstructed northern view for the best experience possible.
Understanding the Risks and Technological Impacts
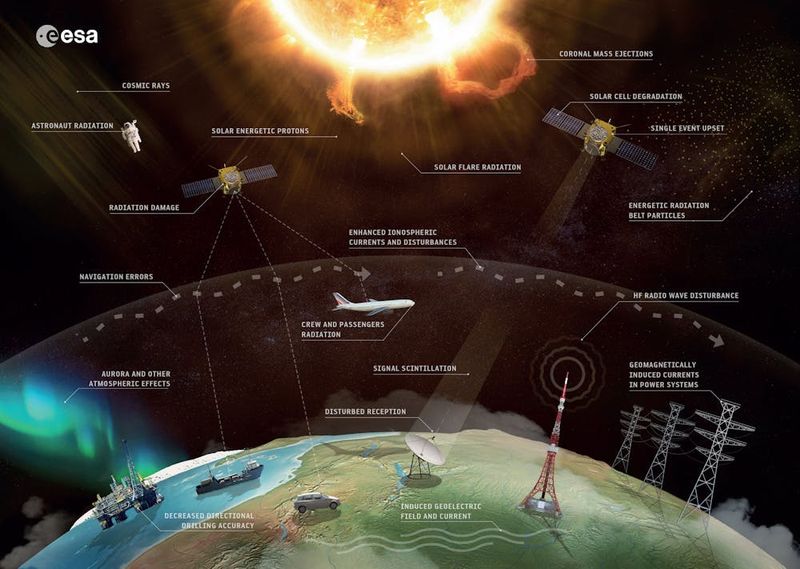
While we’re mesmerized by the beautiful light shows, solar storms pack more than just visual punch. Geomagnetic disturbances can actually mess with our modern technology in surprising ways. Power grids sometimes experience minor fluctuations, satellite communications might get temporarily disrupted, and GPS systems can lose accuracy during intense storms.
Airlines occasionally reroute polar flights during major solar events to avoid communication blackouts and radiation exposure. For most people, these impacts remain barely noticeable, but industries relying on precise positioning or satellite data stay on high alert. That’s why organizations like NOAA constantly monitor space weather and issue warnings. The good news? This week’s G2-level storm is considered moderate, so major disruptions are unlikely. Still, it’s fascinating how the same solar activity creating those stunning auroras can ripple through our technological systems here on Earth.